Bed Bugs

Identifying Bed Bugs
Adult bedbugs are 5mm long. Before feeding they are a flattened oval shape and light brown, but become rounder and darker Adult bed bugs are approximately 5 mm long. Before feeding they are a flattened oval shape and light brown, but become rounder and darker after feeding.Bed bugs do not have wings, but can crawl relatively fast.A bed bug can complete its development from an egg to and adult in as little as 1 month. A single female can potentially produce 200-500 eggs in her lifetime.Adult bed bugs can survive approximately 1 year without feeding; immature bed bugs (nymphs) can go 3-4 months without feeding.Bed bugs are nocturnal, lured from their hiding spots at night by the warmth of our bodies and carbon dioxide in our breath as we sleep.They are typically found in bedrooms, hiding in cracks and crevices during the day. However, they can also be found in other places, such as the living room, where people tend to spend large amounts of time.The most common shelters for bed bugs are in the seams of mattresses, in crevices in the bed frame, behind furniture surrounding the bed (especially the headboard) or where the wall meets the floor.A more established infestation is associated with dark or black staining of the mattress from bed bug excrement.Some reports suggest that an established bed bug infestation will also be associated with an unpleasant odor.
Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites are unlikely to wake the victim. They can occur anywhere on the body but are often close to blood vessels near the skin.A single bed bug may bite more than once around the same area. However, bites in different parts of the body may indicate being bitten by several bed bugs.
Symptoms of bed bug bites vary between individuals. Early in a bed bug infestation, the victim may not yet be sensitized to the bites and therefore may not develop itchy welts.However, small droplets of blood on the sheets may indicate the presence of bed bugs.
Sources of Bed Bug Infestations
Bed bugs usually enter a property carried on clothing, luggage or furniture.The most common source of bed bugs is to stay at a hotel with an infestation. Bed bugs or their eggs get into clothing or suitcases and are then transported home.It is important to check for signs of bed bugs prior to staying in your hotel room. If there are any signs of bed bugs when staying at a hotel, particularly being bitten when sleeping or seeing blood spots on sheets, take great care in bringing your personal belongings home. If you suspect bed bugs, hotel staff should be immediately notified.Consult with hotel management to assess the risk - it may be necessary to launder, fumigate or treat clothes to ensure they are safe. We advise either placing belongings in the freezer or laundering in hot, soapy water and drying in high heat. When moving belongings that may be infested, you should place them in a large garbage bag to lessen the chance of spreading bed bugs throughout your home.You should also inspect all furniture and mattresses that are brought into your home.
Attack Services technicians are skilled, extensively trained and experienced professionals.
They Can provide you with the best and fastest results in removing Bed Bugs. For Help Contact Us On 1300 657 686
Adult bedbugs are 5mm long. Before feeding they are a flattened oval shape and light brown, but become rounder and darker Adult bed bugs are approximately 5 mm long. Before feeding they are a flattened oval shape and light brown, but become rounder and darker after feeding.Bed bugs do not have wings, but can crawl relatively fast.A bed bug can complete its development from an egg to and adult in as little as 1 month. A single female can potentially produce 200-500 eggs in her lifetime.Adult bed bugs can survive approximately 1 year without feeding; immature bed bugs (nymphs) can go 3-4 months without feeding.Bed bugs are nocturnal, lured from their hiding spots at night by the warmth of our bodies and carbon dioxide in our breath as we sleep.They are typically found in bedrooms, hiding in cracks and crevices during the day. However, they can also be found in other places, such as the living room, where people tend to spend large amounts of time.The most common shelters for bed bugs are in the seams of mattresses, in crevices in the bed frame, behind furniture surrounding the bed (especially the headboard) or where the wall meets the floor.A more established infestation is associated with dark or black staining of the mattress from bed bug excrement.Some reports suggest that an established bed bug infestation will also be associated with an unpleasant odor.
Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites are unlikely to wake the victim. They can occur anywhere on the body but are often close to blood vessels near the skin.A single bed bug may bite more than once around the same area. However, bites in different parts of the body may indicate being bitten by several bed bugs.
Symptoms of bed bug bites vary between individuals. Early in a bed bug infestation, the victim may not yet be sensitized to the bites and therefore may not develop itchy welts.However, small droplets of blood on the sheets may indicate the presence of bed bugs.
Sources of Bed Bug Infestations
Bed bugs usually enter a property carried on clothing, luggage or furniture.The most common source of bed bugs is to stay at a hotel with an infestation. Bed bugs or their eggs get into clothing or suitcases and are then transported home.It is important to check for signs of bed bugs prior to staying in your hotel room. If there are any signs of bed bugs when staying at a hotel, particularly being bitten when sleeping or seeing blood spots on sheets, take great care in bringing your personal belongings home. If you suspect bed bugs, hotel staff should be immediately notified.Consult with hotel management to assess the risk - it may be necessary to launder, fumigate or treat clothes to ensure they are safe. We advise either placing belongings in the freezer or laundering in hot, soapy water and drying in high heat. When moving belongings that may be infested, you should place them in a large garbage bag to lessen the chance of spreading bed bugs throughout your home.You should also inspect all furniture and mattresses that are brought into your home.
Attack Services technicians are skilled, extensively trained and experienced professionals.
They Can provide you with the best and fastest results in removing Bed Bugs. For Help Contact Us On 1300 657 686
German Cockroches

Adults are light brown, about 1/2 inch long, sport long antennae and the 2 stripes on their back are usually covered by a pair of thin wings. The teenaged nymphs are slightly smaller and do not have wings.
Cockroaches travel along the edges of walls mostly at night, preferring to congregate in the tiniest of cracks where as much of their body surface can contact safety as possible.
Warm weather accelerates egg laying but a female and her offspring can produce a roach stadium of 30,000 individuals in 1 year. Fortunately for human co-dwellers, cannibalism and lack of sufficient food, water and shelter help to regulate the cockroach population.
Cockroaches travel along the edges of walls mostly at night, preferring to congregate in the tiniest of cracks where as much of their body surface can contact safety as possible.
Warm weather accelerates egg laying but a female and her offspring can produce a roach stadium of 30,000 individuals in 1 year. Fortunately for human co-dwellers, cannibalism and lack of sufficient food, water and shelter help to regulate the cockroach population.
- Oriental Cockroach - 1 ½” - Dark brown to black in color. The wings are undeveloped in female but cover ¾ length of the abdomen in the male; both sexes prefer to run or climb. It prefers cool, damp environments like drains, sewers and crawl spaces.
- American Cockroach - 1 ½” - Also known as the palmetto bug, the American Cockroach is reddish brown in color and has a pale yellow area around the perimeter of the pronotum. These cockroaches tend to be found in dark, undisturbed areas that are high in humidity.
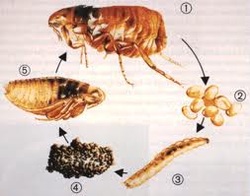
Fleas

All adult fleas suck blood from host animals, usually mammals. These ectoparasites are well-equipped for life on a furry food source. A hungry flea in search of a bloodmeal uses its maxillary blades to puncture the skin of its host. A bit of flea spit keeps the blood from clotting while the parasite assembles its siphon, using modified mouthparts which form a tube.
Fleas live wherever you find mammals, throughout the world,
Fleas have evolved into wingless arthropods. Their only need for locomotion is to land on a host, and for that they've developed superior jumping abilities. Fleas can launch themselves quite high in the air, up to 80 times their own height. In addition to strong rear legs designed for jumping, fleas have a substance called resilin above the hind legs. This rubbery substance compresses as the flea prepares to jump, storing potential energy. When the flea thrusts upward, this energy is converted to kinetic energy, the energy of motion.
Fleas live wherever you find mammals, throughout the world,
Fleas have evolved into wingless arthropods. Their only need for locomotion is to land on a host, and for that they've developed superior jumping abilities. Fleas can launch themselves quite high in the air, up to 80 times their own height. In addition to strong rear legs designed for jumping, fleas have a substance called resilin above the hind legs. This rubbery substance compresses as the flea prepares to jump, storing potential energy. When the flea thrusts upward, this energy is converted to kinetic energy, the energy of motion.
RedBack Spider

Redback spiders feed mainly on ground-living insects that blunder into their webs, but small vertebrates such as lizards and even mice can fall victim.
Also eaten - after mating - are the tiny male redbacks.
A female redback spider can produce eggs for up to two years after a single mating. Eggs are enclosed in 3-5 dirty-white, woolly, spherical egg sacs suspended in the retreat of the web and guarded by the female.
Spiderlings emerge after about 14 days and disperse on the wind as soon as conditions are right. This is how redback spiders turn up in new places or quickly recolonise areas from which they have previously been removed.
Also eaten - after mating - are the tiny male redbacks.
A female redback spider can produce eggs for up to two years after a single mating. Eggs are enclosed in 3-5 dirty-white, woolly, spherical egg sacs suspended in the retreat of the web and guarded by the female.
Spiderlings emerge after about 14 days and disperse on the wind as soon as conditions are right. This is how redback spiders turn up in new places or quickly recolonise areas from which they have previously been removed.
Funnel-Web Spider

The Sydney Funnel-web spiders are some of the world’s most deadly spiders.
There are many species of funnel-web spiders found throughout Australia. Some are dangerous, some are not. The northern,
or tree dwelling, funnel-web spider is not often seen but it is very poisonous. Other species of funnel-webs that live in southern parts of Australia are not dangerous.
There are many species of funnel-web spiders found throughout Australia. Some are dangerous, some are not. The northern,
or tree dwelling, funnel-web spider is not often seen but it is very poisonous. Other species of funnel-webs that live in southern parts of Australia are not dangerous.
- Some funnel-web spiders live in trees.
- Sydney funnel-web spiders live in holes in the ground.
Sydney funnel-web spiders are large black spiders with big powerful fangs, which can be up to 7 millimetres long. The body of the female is about 3.5 centimetres long.
The male is smaller and about 2.5 centimetres long. Their bodies are covered with fine hairs and they have shiny legs.
Male Sydney funnel-web spiders are Australia's most dangerous spider. These aggressive spiders grab onto their victims and bite several times, injecting a very poisonous venom. Some people have died from the bite of these spiders.
Where do Sydney funnel-web spiders live?
Sydney funnel-web spiders live in and around Sydney, in New South Wales, Australia. They live in small, neat holes lined with a collar of silk. The holes are made in shady
places under rocks, shrubs, logs and leaf litter. Silk threads lead away from the entrance to the burrow. These are trip lines and when prey walks into them, the spider dashes out of the burrow to grab it. The spider bites the prey and takes it back into the burrow to eat. Funnel-web spiders prey on and eat beetles, cockroaches, insect larvae, snails,millipedes and sometimes even small frogs and lizards.
Life Cycle
A female mates with a male spider and then lays from 80 to 200 yellow-green eggs, which she wraps in a silk egg sac. She keeps the sac inside her burrow and guards it until the young spiders, called spiderlings, hatch about three weeks later. The spiderlings share their mother's burrow for a few weeks before wandering off to find a place of their own to live. Males die a few months after mating but females can live and breed for several years.
Can funnel-webs swim?
Wandering funnel-webs spiders often fall into backyard swimming pools and they can stay alive for hours. They can't swim but they can trap a small bubble of air in hairs around the abdomen, which aids both breathing and floating, so it should not be assumed that a spider on a pool bottom has drowned. As they gradually get waterlogged, their buoyancy decreases and they eventually sink and drown. Funnel-webs have been known to survive 24-30 hours under water.
Can funnel-webs jump?
Despite what many people think, funnel-webs can' t jump. However they can move quickly, and they will rear up when irritated and make sudden lunges when striking
The male is smaller and about 2.5 centimetres long. Their bodies are covered with fine hairs and they have shiny legs.
Male Sydney funnel-web spiders are Australia's most dangerous spider. These aggressive spiders grab onto their victims and bite several times, injecting a very poisonous venom. Some people have died from the bite of these spiders.
Where do Sydney funnel-web spiders live?
Sydney funnel-web spiders live in and around Sydney, in New South Wales, Australia. They live in small, neat holes lined with a collar of silk. The holes are made in shady
places under rocks, shrubs, logs and leaf litter. Silk threads lead away from the entrance to the burrow. These are trip lines and when prey walks into them, the spider dashes out of the burrow to grab it. The spider bites the prey and takes it back into the burrow to eat. Funnel-web spiders prey on and eat beetles, cockroaches, insect larvae, snails,millipedes and sometimes even small frogs and lizards.
Life Cycle
A female mates with a male spider and then lays from 80 to 200 yellow-green eggs, which she wraps in a silk egg sac. She keeps the sac inside her burrow and guards it until the young spiders, called spiderlings, hatch about three weeks later. The spiderlings share their mother's burrow for a few weeks before wandering off to find a place of their own to live. Males die a few months after mating but females can live and breed for several years.
Can funnel-webs swim?
Wandering funnel-webs spiders often fall into backyard swimming pools and they can stay alive for hours. They can't swim but they can trap a small bubble of air in hairs around the abdomen, which aids both breathing and floating, so it should not be assumed that a spider on a pool bottom has drowned. As they gradually get waterlogged, their buoyancy decreases and they eventually sink and drown. Funnel-webs have been known to survive 24-30 hours under water.
Can funnel-webs jump?
Despite what many people think, funnel-webs can' t jump. However they can move quickly, and they will rear up when irritated and make sudden lunges when striking